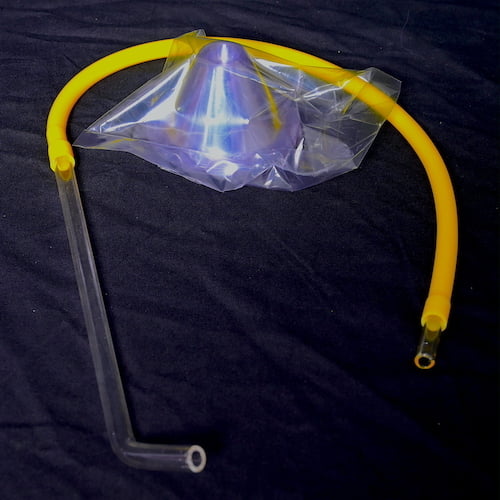
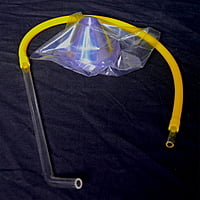

Bioassay WHO Cones Kit Includes Aspirator
Bioassay cones for testing shelf life of an insecticide onto various physical surfaces. Package contains 10 cones. The list price is for 10 cones. Only cones, the kit does not include surfaces. You can order different surfaces separately for conducting bioassays.
The cone bioassay is a controlled test to measure insecticide effectiveness, particularly in mosquito nets. It uses specialized cones where mosquitoes are exposed to treated material or a control. After exposure, researchers monitor mortality rates to assess the insecticide's impact. This standardized procedure helps ensure mosquito nets remain potent weapons against malaria by evaluating their ability to kill or knock down insects.
Customize
Product Details
The WHO Cone Bioassay plays an integral role in the evaluation of the efficacy of long-lasting insecticidal nets as well as insecticides used in indoor residual spraying. The test is used on a variety of treated substrates, such as pieces of bed nets, mud, cement and wood. The package consists of plastic cones only. The additional requirements to perform cone bioassay like the solid surfaces, treatment materials, clips, cotton plugs and others are to be purchased separately as this can't be considered in general to list the items here for the purchase.
Cone dimensions:
Diameter: 12 cm
Height: 9 cm
Volume: 180 cm3
Cone Bioassay Procedure
The cone bioassay is a standardized test used to assess the effectiveness of insecticides, especially those applied to mosquito nets. Here's a breakdown of the typical procedure:
Materials:
WHO-specified bioassay cones (12 cm diameter, 9 cm height)
Holding cages or cups for mosquitoes
Aspirator for transferring mosquitoes
Bungs for sealing cone openings
Timer
Insecticide-treated material (e.g., net sample)
Control material (untreated net sample)
Mortality recording sheet
Preparation:
Mosquito Selection: Use healthy, non-blood fed, female mosquitoes of the target species (usually malaria-transmitting mosquitoes).
Material Preparation: Cut appropriate test pieces from the insecticide-treated material and control material according to the specific protocol.
Test Procedure:
Negative Control: Introduce a set number of mosquitoes (often 5) into a cone containing the untreated control material. Seal the cone with a bung and start the timer.
Treatment Groups: Repeat step 1 for each cone containing a test piece of the insecticide-treated material. Ensure separate aspirators are used for treated and control groups to avoid contamination. Introduce mosquitoes into each cone sequentially, allowing a short interval (e.g., 1 minute) between each introduction.
Exposure: After all mosquitoes are introduced, leave them exposed to the material for a specified duration (usually 30 minutes to 1 hour).
Post-Exposure: Transfer the mosquitoes from each cone back to their designated holding cages and monitor them for mortality over a set period (typically 24 hours).
Data Collection:
Record the number of knocked down (KD) mosquitoes at specific intervals during exposure (e.g., every 10 minutes).
Record the number of dead mosquitoes after the monitoring period.
Analysis:
Calculate the mortality rate for each treatment group and the control group.
Compare the mortality rates between treated and untreated groups to assess the effectiveness of the insecticide.
Additional Considerations:
Maintain consistent temperature and humidity throughout the experiment.
Use proper handling techniques to minimize stress on the mosquitoes.
Perform the bioassay with replicates for each treatment and control group to ensure statistical significance.
Follow specific protocols and guidelines set by organizations like the WHO for accurate and reliable results.
By following this procedure, researchers can evaluate the efficacy of insecticides and ensure long-lasting insecticidal nets remain effective in controlling mosquito populations.
Please visit here to buy WHO adult susceptibility kit
bioassay cone test kit India, mosquito cone test apparatus supplier, insecticide bioassay cone test kit online, vector biology testing equipment India, WHO cone bioassay product India, lab equipment for mosquito resistance testing, cone test mosquito assay India, buy WHO cone test for entomology research, cone bioassay test WHO guideline kit, buy bioassay cone test kit for vector-borne disease research, field-use mosquito bioassay test kit, laboratory mosquito insecticide testing cones, cone test kit for pyrethroid resistance testing, bioassay cone kit for DDT susceptibility test, public health insecticide testing kit, WHO standard cone test for mosquito control programs, mosquito insecticide effectiveness testing cones, bioassay cone test kit for ICMR vector control units, WHO cone bioassay kit for NVBDCP India, bioassay cone test kit for NIMR labs, cone test for VCRC Puducherry, insecticide resistance cone test for NCDC Delhi, bioassay cone test kit for PHFI researchers, mosquito control research equipment India, cone test kit for state health departments, bioassay test cones for medical colleges, cone bioassay kit for entomology departments, bioassay cone test kit for mosquito research, WHO cone bioassay kit India, mosquito insecticide resistance test kit, vector control bioassay cone kit, WHO bioassay cone test equipment, mosquito bioassay cone test supplier India, cone test for vector control labs, bioassay cone test for malaria research, insecticide susceptibility testing cones, dengue vector bioassay cone kit, vector biology bioassay test cones, Aedes mosquito resistance testing kit, WHO bioassay test kit for research centres, bioassay cone test kit for Culex mosquito, Anopheles bioassay cone kit India, malaria entomology test cones India