Large insect containers serve as valuable tools for qualified entomologists in conducting comprehensive studies, observations, and research on insects. Here we list a few of the most useful cases where these insect containers are useful for conducting entomological research and a general insect research:
Habitat Replication: These insect containers enable the meticulous replication of natural habitats, allowing for precise investigations into insect behavior, reproduction, and ecology under controlled conditions. These containers integrate simulated landscapes, vegetation, and microclimates, facilitating the emulation of specific ecosystems for in-depth analyses.
Long-term Observation: These containers support prolonged observations, enabling longitudinal studies on population dynamics, seasonal fluctuations, and life cycle progression. Through meticulous observation, researchers can discern behavioral patterns, inter-species interactions, and phenotypic variations over extended periods.
Experimental Manipulation: Large containers provide ample space for intricate experimental designs, allowing researchers to introduce controlled environmental stressors, manipulate resource availability, or investigate the impact of various chemicals or treatments on insect physiology and behavior.
Breeding and Rearing: The insect containers accommodate insect colonies for breeding and rearing purposes, providing the necessary space for mating, oviposition, and larval development. Researchers can produce successive generations of insects for further experimentation or field release.
Biodiversity Studies: These containers serve as microcosms for biodiversity studies, enabling researchers to collect and observe multiple insect species within a confined space. This facilitates rigorous analyses of species richness, abundance, and community dynamics, providing valuable insights into ecosystem functioning and resilience.
Educational Outreach: Large insect containers are invaluable educational tools, offering immersive learning experiences for students and the general public. These containers enable hands-on observation of insects, fostering a deeper understanding of their biology, ecology, and ecological significance.
Bioassays and Toxicology Studies: The containers are employed for conducting precise bioassays and toxicology studies, evaluating the effects of pesticides, pollutants, or environmental contaminants on insect health, survival, and behavior.
Insectary Research: In specialized insectaries, large containers are used to establish and maintain insect colonies for sophisticated research endeavors. These containers facilitate investigations into intricate aspects of insect biology, including insect-plant interactions, insect physiology, and insect-pathogen relationships.
In summary, large insect containers are indispensable instruments for conducting sophisticated experiments, precise observations, and rigorous research in both laboratory and field settings.
When selecting insect containers, several important points should be considered to ensure the suitability and effectiveness of the containers for the intended purpose. Here are the main points to keep in mind:
Size and Capacity: Choose containers that provide ample space for the insects being studied, considering factors such as the size, number, and behavior of the insects. Ensure that the containers have sufficient capacity to accommodate the insects comfortably without overcrowding. Outnumber of insects than the capacity of the insect containers results in death of insects
Material: Select containers made from either glass or plastic. Transparent containers allow for easy observation of the insects without the need to disturb them, while durable materials ensure longevity and resistance to damage.
Ventilation: Ensure that the containers provide adequate ventilation to maintain airflow and prevent the buildup of moisture, which can lead to mold growth or respiratory issues for the insects. Look for containers with built-in ventilation holes or mesh screens to facilitate airflow. Different ventilations might also be useful since different insects have varied requirements when it comes to moisture. Also, it is important to take note that whether the insects are going to be raised on artificial food or natural plant materials.
Escape Prevention: Choose containers with secure closures or lids to prevent the escape of insects. Look for containers with tight-fitting lids or sealing mechanisms that minimize the risk of insects escaping and contaminating the environment. Also few of the times when containers are intended for transporting insects from field to field or field to lab or lab to field or simply one location to another location it is important to consider the containers with tight lids
Accessibility: Consider the ease of access to the insects within the containers for observation, feeding, and maintenance. Select containers with convenient openings or access points that allow for easy handling of the insects without causing stress or injury. For example easy to remove aeration holes acts as both aeration holes as well as feeding point.
Stackability and Storage: If multiple containers will be used, consider containers that are stackable for efficient storage and space utilization. Stackable containers help optimize storage space and organization, especially in limited laboratory or storage environments. This is especially useful when intension is to raise multiple insect colonies to be raised for specific research objectives
Cost and Budget: Evaluate the cost-effectiveness of the containers relative to the research budget and long-term maintenance requirements. Balance the upfront cost of the containers with their durability, functionality, and suitability for the intended use. We have several containers few are durable and others last short term.
Different types of containers specifically used for housing, storing, breeding and observing insects. Here are revised types of insect containers and their uses:
Glass Jars: Glass jars with lids are versatile containers used for short-term insect storage and observation in laboratory settings. They provide a clear view of the insects and are suitable for a wide range of insect species. These contains are suitable for repeated use however there are high chances that mis handling might broke the containers.
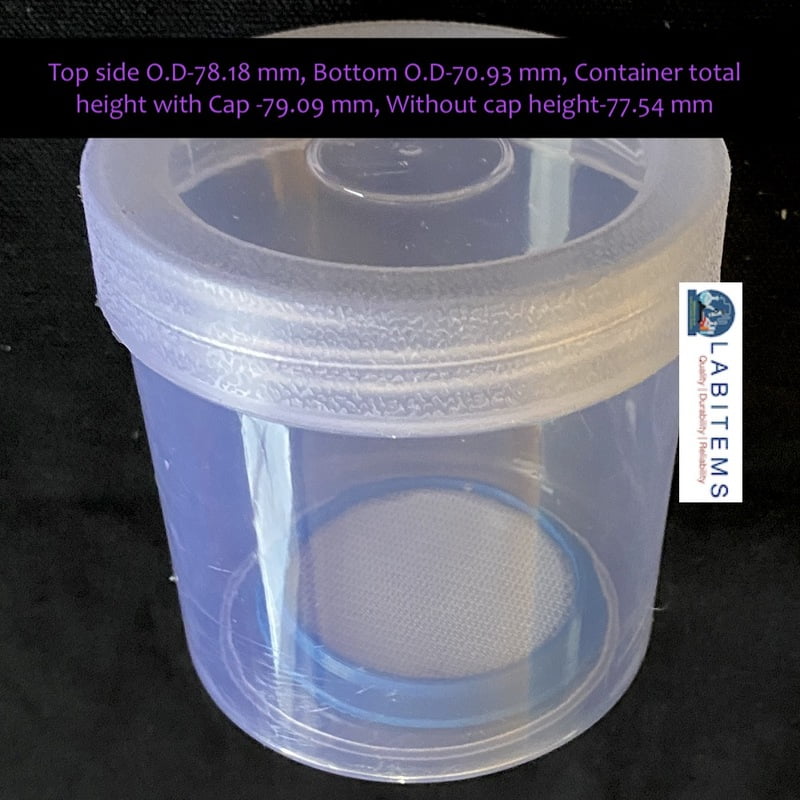
Plastic Containers: Plastic containers with secure lids are lightweight and durable options for insect storage and transport. They come in various sizes and shapes and are commonly used for field collection, laboratory studies, and insect rearing. Even though the containers can be used repeatedly, the lids broke due to repeated use. These are economical containers too.
Mesh Cages: Mesh cages made from fine mesh fabric provide ventilation and airflow while containing insects. They are ideal for housing live insects in laboratory settings and can be used for breeding, observation, and experimentation. These are durable and can be used repeatedly.
Petri Dishes: Petri dishes are shallow, circular containers made from acyrlic plastic. They are commonly used for short-term observation and experimentation, such as studying insect behavior, feeding preferences, or development stages. These contains are durable and can be used repeatedly.
Vials, and Tubes: Small vials or tubes with screw caps are used for storing individual insects or small specimens. They are convenient for field collection and storage of delicate or tiny insects, such as parasitic wasps or beetles. We have containers from 25ml to 200ml are available. These containers can be repeatedly be used.
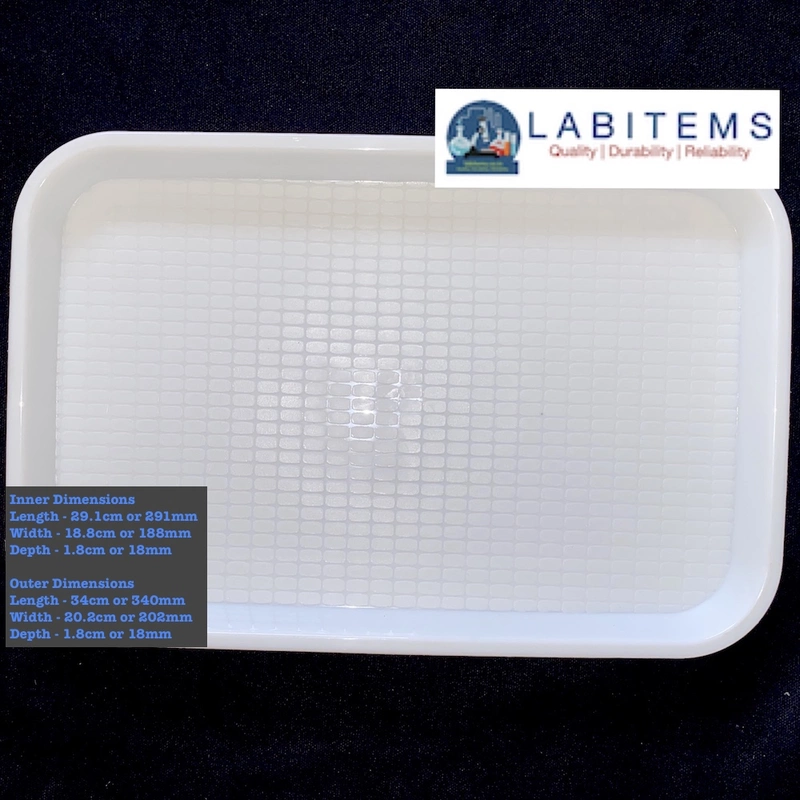
Insect Rearing Trays: Rearing trays or containers with multiple compartments are used for rearing insect colonies in laboratory settings. They provide separate chambers for different developmental stages or experimental treatments, facilitating controlled studies and breeding programs. These trays are also used for conducting bioassay studies on insects. Different well type of containers are available for use.
Flight Cages: Flight cages are large enclosures equipped with mesh walls or netting that allow insects to fly freely while containing them within a controlled environment. They are used for studying flight behavior, navigation, and dispersal of insects. These type of open cages are usually used to study flying and highly motile insects.
Aquatic Containers: Containers designed for aquatic insects include aquariums, tanks, or trays filled with water and aquatic plants. They are used for studying aquatic insect species, including larvae, nymphs, and adults, in their natural habitat.