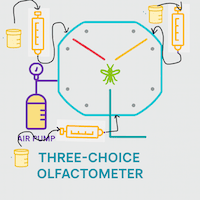
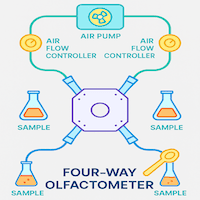
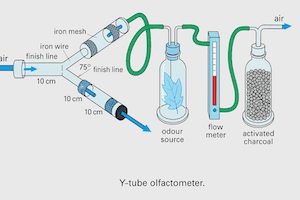
Role of Air Delivery System in Generating Reproducible Results
The Importance of Airflow Controllers in Insect Olfactometers
Insect olfactometers are indispensable tools in entomological research, facilitating investigations into the olfactory behaviors of insects. Central to the efficacy of an olfactometer setup is an airflow controller. Our aim here is to emphasize the significance of an airflow controller in insect olfactometers by presenting a detailed analysis complemented by pertinent examples.
- Delivery of Odor Stimuli: Ensuring the consistent and directed flow of odorous stimuli to the test insect is paramount. An airflow controller guarantees this precision. For example, in research on the attraction of female mosquitoes (e.g., Anopheles gambiae) to human odors, consistent delivery enabled researchers to identify specific compounds that elicited strong behavioral responses. These responses might be negative or positive like attraction towards the scents. In contrast, improper and uncontrolled air delivery system or no delivery system poses challenges to deliver consistent odors to the test chamber. Also, accumulation of odors at specific constricted junctions is possible which makes the experimental results questionable.
- Control of Odor Concentration: By adjusting the airflow, researchers can precisely modulate the concentration of the introduced odor. This is crucial in studies determining behavioral thresholds. For instance, experiments with the grapevine moth (Lobesia botrana) demonstrated that varying concentrations of certain pheromones could either attract or repel the moth, emphasizing the importance of precise concentration control. Furthermore, before optimizing the odor concentrations, using the olfactometer with good flow control systems we can determine the closest minimal concentration that can elicit insect responses.
- Prevention of Stagnation: Consistent airflow mitigates the risk of odor stagnation. Without it, volatile compounds might accumulate, potentially skewing results. A study involving the Western Corn Rootworm (Diabrotica virgifera virgifera) showed that accumulation of certain volatiles over time significantly altered their behavior within the olfactometer. Accumulation of volatiles will change the concentration of available volatiles available for the insects' responses. It means that in the absence of control air delivery system, the odors might stagnate at the junctions of the constrictions and add a variation to the experiment. In such cases, results of the experiments can’t be reproduced with confidence. Also, change of olfactometer model for experiment might introduce variation into the system due to different constrictions and free flow areas of the design. Hence, prevention of stagnation of volatiles or odors is very important to get consistent results.
- Control of Background Odors: Ensuring a background odor-free environment is essential. For example, in experiments assessing the responses of the honeybee (Apis mellifera) to floral scents, maintaining a neutral olfactory background was crucial for isolating specific responses to individual compounds. When proper delivery system is not available or not used for the olfactometer, there will be other unwanted or unknown scents enter into the system and that might add variation to the experiment.
- Regulation of Humidity and Temperature: Factors like humidity and temperature, influenced by airflow, have known impacts on insect behavior. In a study on the Asian citrus psyllid (Diaphorina citri), researchers found that variations in humidity levels drastically affected the insect's response to citrus volatiles. Since temperature and humidity negatively influences mosquitoes or other insects to a great extent that that can even kills the experimental insects. The insect olfactometer temperature can be controlled by conducting experiments in temperature-controlled test rooms like the rooms with a functional air conditioner. The humidity can also alter the experimental results. Controlling humidity while experimenting with the odors should be considered important for consistent results.
- Directing Insect Movement: Controlled airflow can guide insect movement, enhancing interpretability. For instance, in a Y-tube olfactometer study on fruit flies (Drosophila melanogaster), controlled airflow was crucial in ensuring that observed preferences for certain fruity odors were genuine and not due to random movement. When air flow is available, insects sense the odors consistently hence acts as a cue. In the absence of power-controlled air flow, it may be noted that the cues are not consistent as air speed is not constant which in fact carries the odors to the test chamber. This confuses the insect moment to a certain extent and certainly this issue can add an experimental variation which may result in inconsistent experimental outcomes.
- Replicability and Consistency: Consistent conditions afforded by airflow controllers bolster the replicability of experiments. This becomes vital when comparing results across multiple studies, ensuring that any observed differences in behavior are due to the variables being tested rather than inconsistencies in the testing environment.
- Safety Measures: In certain experiments, toxic or harmful substances might be used. An airflow controller ensures safety by preventing the buildup of harmful concentrations. For example, in experiments studying insect responses to pesticides or other toxic volatiles, controlled airflow protected both the test subjects and the researchers from potential harm.
In summation, an airflow controller's role in insect olfactometers extends beyond mere functionality. It ensures precision, safety, and the overall robustness of entomological investigations.