Albert Stain A or B solution for microbiological staining
In the Albert's staining procedure, after the smear is prepared and heat-fixed, Albert's stain A is applied first, followed by a wash, and then Albert's stain B is applied. The combination of these two stains allows for the differential visualization of the metachromatic granules in the bacterial cells.
Albert's stain is a differential staining technique, and it utilizes two staining solutions: Albert's stain A and Albert's stain B.
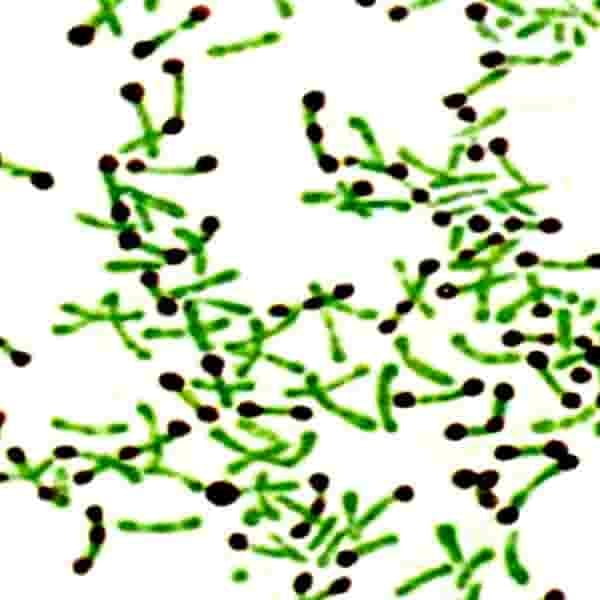
Albert's stain A: This is primarily toluidine blue. When applied to a bacterial smear, it imparts a greenish color to the bacterial cells. The metachromatic granules (like the Volutin granules in Corynebacterium diphtheriae) have the capacity to change the color of certain dyes, so when toluidine blue (from Albert's stain A) comes into contact with these granules, it changes from green to a blue or purple color.
Albert's stain B: This is an iodine solution that acts as a mordant in this staining process. A mordant is a substance that helps set or stabilize dyes on the microbial cell, increasing the affinity between the dye and the cell. When Albert's stain B is applied, it helps in the fixation of the toluidine blue dye, allowing for better visualization of the metachromatic granules.
In the Albert's staining procedure, after the smear is prepared and heat-fixed, Albert's stain A is applied first, followed by a wash, and then Albert's stain B is applied. The combination of these two stains allows for the differential visualization of the metachromatic granules in the bacterial cells.
Here's a brief overview of the staining procedure:
- Prepare a smear of the bacterial culture.
- Air dry and heat fix.
- Apply Albert's A stain (toluidine blue) and let it sit for a few minutes.
- Rinse with water.
- Apply Albert's B stain (iodine solution) as a mordant and allow it to act for a few minutes.
- Rinse with water.
- Observe under the microscope.
After staining, the metachromatic granules appear blue or purple, while the rest of the bacterial cell is green.
It's important to note that this stain is not widely used in routine diagnostic microbiology anymore, but it still holds educational value and can be used in specific research contexts.